The Importance of Order Types
Order types are essential for implementing an effective investment strategy, as they help achieve fair prices for buying and selling securities and prevent significant losses. Investors can choose from a variety of Order Types, each offering different execution parameters in terms of price. These options support strategy implementation by setting parameters like limit-stop, loss thresholds, and maximum prices.
When selecting a broker and trading platform, it’s important to consider that not all order types are available on every platform or with every broker. Additionally, some brokers may charge high fees for special order types, making it crucial to weigh these costs. By understanding and utilizing the appropriate order types, investors can enhance their trading strategies and make more informed decisions.
Table of Contents
Market Order
A Market Order is an instruction to your broker to execute a trade immediately at the best available price. These orders are usually completed very quickly, provided there is enough market liquidity. Once executed, a Market Order is referred to as a “filled order.” Market Orders are particularly useful when the speed of execution is more important than the price, often used by traders looking to enter or exit the market swiftly, especially in volatile conditions. However, it’s crucial to note that the actual executed price may differ from the last displayed price, especially during sudden market movements. Therefore, while Market Orders can be effective, they should be used with caution, particularly for large positions or in markets with low liquidity to avoid unexpected price changes.
Example
If the current market price is 100 USD, a buy or sell market order will be executed at approximately 100 USD.

Limit Order
Limit Orders are a valuable tool in the arsenal of any trader. They allow investors to set a minimum price for selling or a maximum price for buying an asset, ensuring that the trade will not execute at a price worse than the set limit. This feature provides a layer of control and precision, protecting traders from unfavorable market fluctuations. If the specified price is not achievable at the time the order is placed, the order is sent to the trading venue where the best price execution is expected. By leveraging limit orders, traders can enhance their strategy and potentially maximize their returns while minimizing risk.
Example
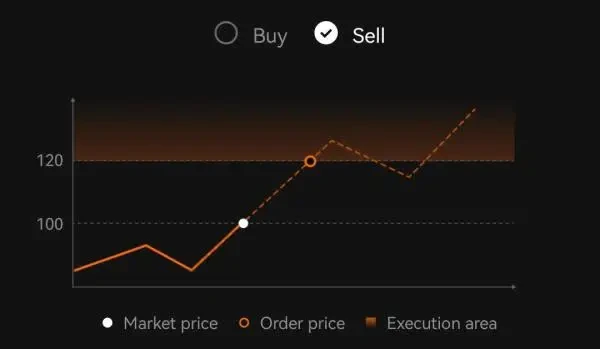
Buy Order: If the current market price is 100 USD, a buy limit order at a price of 80 USD will only be executed if the market price falls to 80 USD or below.
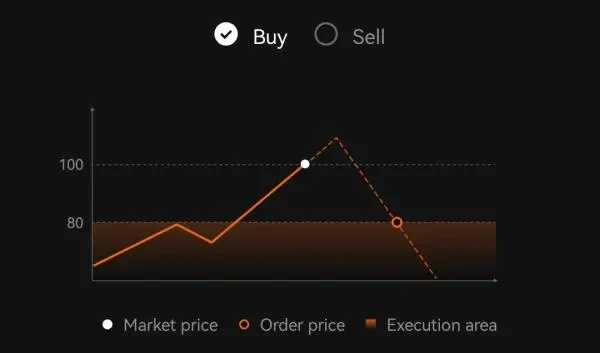
Sell Order: If the current market price is 100 USD, a sell limit order at a price of 120 USD will only be executed if the market price rises to 120 USD or above.
Stop-Loss Order
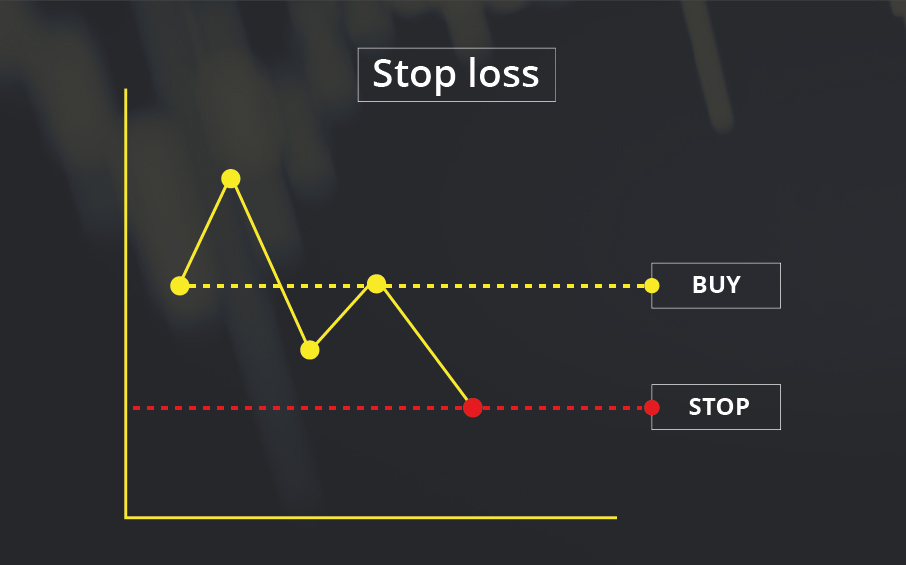
A Stop-Loss Order is an essential risk management tool for investors. By setting a stop-loss level, investors establish a price threshold. If the stock price falls to or below this level, a Market Order is automatically triggered. This Market Order instructs the broker to sell the stock immediately at the best available price. Utilizing stop-loss orders helps investors limit losses and secure gains already achieved, providing a safeguard against significant market downturns and enhancing overall investment strategy.
Stop Limit Order
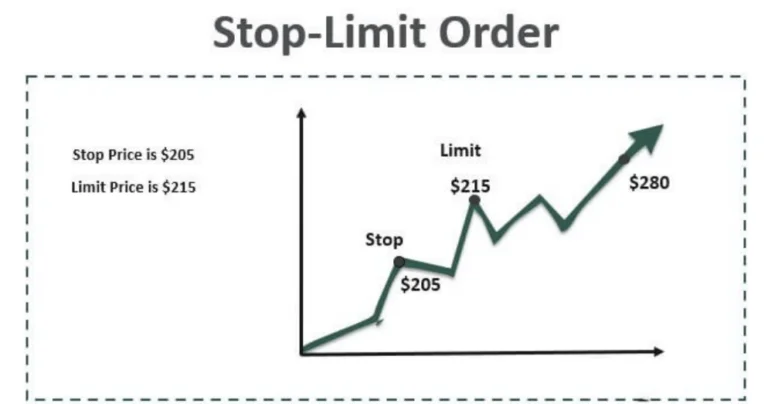
A Stop Limit Order is an advanced version of classic stop orders, providing greater control over both purchases and sales. This type of order only triggers if the price of the underlying asset is between the stop price and an upper limit for buying or a lower limit for selling. While this order type offers precision, it also contains a risk: if the price falls below the lower limit, the sale is not executed. This can lead to potential losses increasing if the price continues to fall below the set limit. Using stop limit orders can help fine-tune your trading strategy while being mindful of associated risks.
Trailing-Stop Order
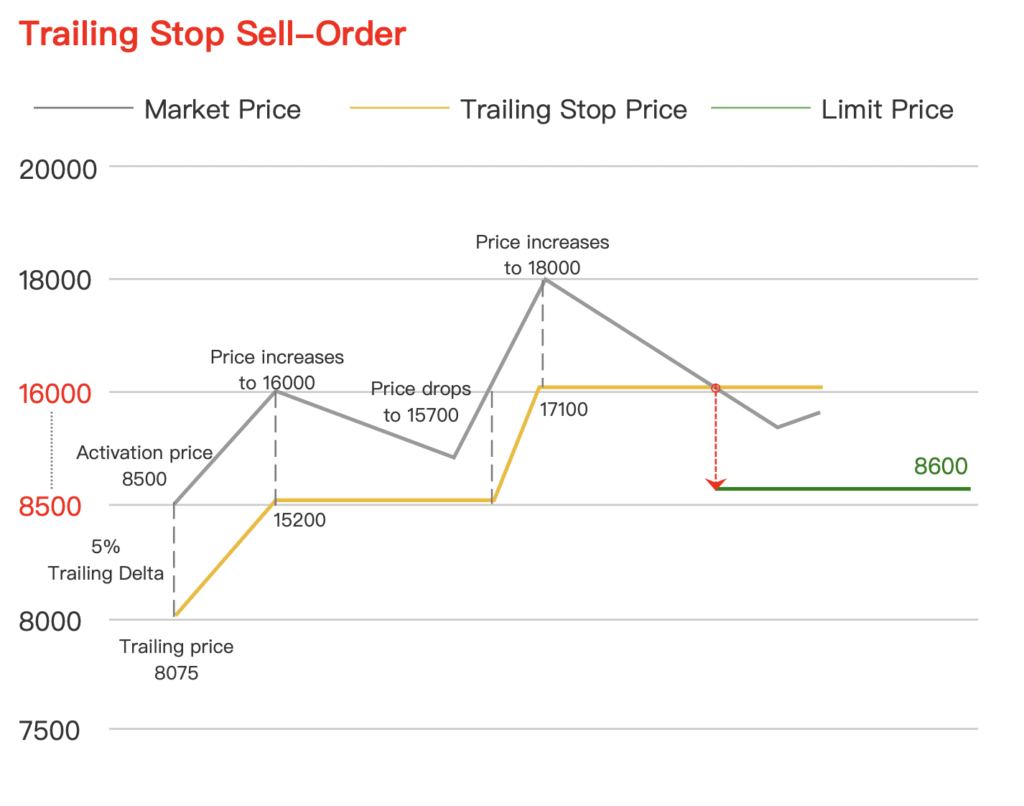
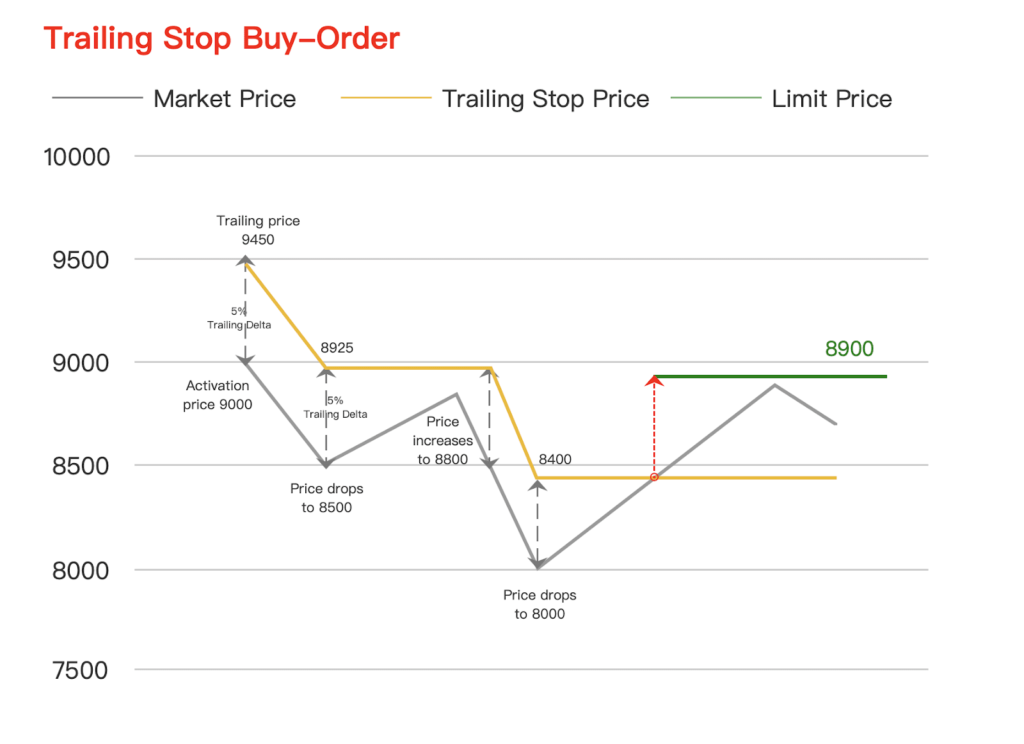
A Trailing-Stop Order is a special type of stop order that automatically adjusts to secure profits when the market price rises. If the market price falls, the stop price remains unchanged and closes the position if the market moves unfavorably. Instead of a fixed stop price, a specific trailing distance from the current market price is set. For a long position, the trailing-stop order is set below the current market price, while for a short position, it is set above the current market price. Investors can set the trailing stop as a percentage or absolute value from the market price, known as the Trailing-Step. This dynamic adjustment helps maintain the specified trailing distance relative to the market price, ensuring that profits are locked in as the market moves in a favorable direction.
Trailing-Stop Sell Order:
Trailing-Stop Buy Order:
Fill-or-Kill (FOK) Order
A Fill-or-Kill (FOK) Order is a specific order type for securities transactions that must be executed immediately in full or be canceled. This “extreme order” is typically used for trading large quantities of stocks with a limit for same-day execution. The primary purpose of an FOK order is to ensure that a whole position is executed quickly at current prices, preventing the potential for market price fluctuations that could occur with the gradual execution of a large order. Although an FOK order demands immediate full execution, partial execution may occur depending on the exchange, providing a rapid and efficient method for large trades.
Good ‘Til Cancelled (GTC) Order
Traders have the flexibility to specify various order types to suit their needs. A Day Order is valid until the end of the trading day, ensuring that if not executed, it expires at market close. An IOC Order (Immediate Or Cancel Order) must be executed immediately or canceled, providing an efficient option for time-sensitive trades. For longer durations, a GTC Order (Good Til Cancelled Order) remains active until executed or canceled by the trader. This allows traders to place an order days or weeks in advance of reaching a specific price level, making it particularly useful for Limit Orders and Stop Orders due to its extended validity. Order customization enhances trading strategies by offering tailored solutions to meet diverse investment goals and market conditions.
Immediate or Cancel (IOC) Order
An IOC Order (Immediate-or-Cancel) can only be placed on the Xetra trading platform. This order type ensures that the trade is executed immediately and as fully as possible. Any unexecuted portion of the order is canceled and not entered into the order book, making it suitable for investors who want their order to be executed even if only partially, under the specified conditions. The execution of an IOC order can consist of multiple partial executions, providing a flexible and efficient solution for investors looking to optimize trade execution under time-sensitive market conditions.
Order Types pros and cons
| Order Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Market Order | Immediate execution – Ensures trade is completed – Good for quick entry/exit | Executed price may differ from expected – Not suitable in volatile markets or low liquidity situations |
| Limit Order | Control over execution price – Protects against unfavorable price fluctuations – Enhances trading strategy | May not be executed if the set price is not reached – Potentially slower execution |
| Stop-Loss Order | Limits potential losses – Secures gains automatically – Essential for risk management | Executed as a Market Order, may sell at a lower price than expected – Not effective in rapidly falling markets |
| Stop Limit Order | Greater control over execution price range – Protects against large losses – Useful for precise trading strategies | Risk of non-execution if the price falls below the limit – Can result in larger losses if the market moves unfavorably beyond the set limits |
| Trailing-Stop Order | Secures profits as market price rises – Automatically adjusts to favorable market movements – Dynamic and flexible | May trigger too early if market price fluctuates – Requires careful setting of trailing distance to avoid premature stop |
| Fill-or-Kill (FOK) Order | Ensures immediate and full execution or no execution – Prevents partial fills – Useful for large orders to avoid price fluctuations | May result in no execution if the full quantity is not available – Not suitable for smaller, less urgent trades |
| Good ‘Til Cancelled (GTC) Order | Stays active until executed or canceled – Useful for long-term trading strategies – Convenient for setting and forgetting orders until target price is reached | May remain open for a long time, potentially causing oversight – Requires periodic review to ensure relevance with current market conditions |
| Immediate or Cancel (IOC) Order | Ensures immediate execution – Flexibility with partial fills – Good for time-sensitive trades | Unexecuted portion is canceled – May not achieve full quantity desired, leading to potential incomplete trades |
Disclaimer: This information material (regardless of whether it reflects opinions or not) is intended solely for general information purposes. It does not constitute independent financial analysis and is not financial or investment advice. It should not be relied upon as a decisive basis for an investment decision. This information material is never to be understood as GlazHome/CostGame recommending or deeming the acquisition or disposal of certain financial instruments, a particular timing for an investment decision, or a specific investment strategy suitable for any particular person. In particular, the information does not take into account the individual investment goals or financial circumstances of any individual investor. The information has not been prepared in accordance with the legal requirements designed to promote the independence of financial analysis and is therefore considered a marketing communication. Although GlazHome/CostGame is not expressly prevented from acting before providing the information, GlazHome/CostGame does not seek to gain an advantage by disseminating the information beforehand.




Pingback: Introduction to Trading Terminology - Glaz Home